By Schneider Electric (China) Investment Co., Ltd., Feng Chenghua
By Qinghai Oilfield Company, Oil Production Plant No.1, Sun Lirong
At present, with the increasing application of busbar trunking systems in power distribution systems, their safety has attracted much attention. The safety of the grounding system of the busbar trunking system is a very critical part of it.
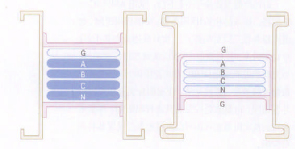
There are two practices of grounding system of busbar trunking system at present. The grounding system of the busbar is to use the independent conductor as the PE grounding wire, thus forming the TN-S grounding system together with the phase line and the neutral line. The essence of the PE grounding wire is to provide an independent and effective grounding path for the entire busbar trunking system. At present, many busbar trunking grounding systems have been specified and required, such as UL857(Chapter 5 Enclosure, Chapter 37 Electrical connections and Chapter 51 Short-circuit tests), IEC439(Chapter 8 Electrical connections) and GB7251(Chapter 7 Design and structure and Chapter 8 Type tests) and so on. In the entire busbar trunking industry, the practice of the grounding system can be mainly divided into the following two types. 1) Internal independent grounding type busbar (ING, see Figure 1). That is, an independent conductor (usually 50% grounding capacity) is added inside the busbar trunking system as an independent PE line, which is formed with the phase line and the neutral line busbar to form the TN-S grounding system. This grounding system is also called the traditional grounding system. 2) Overall grounding type busbar (IGB, see Figure 2). That is, the entire/partial shell of the busbar trunking system is used as an independent PE line (50% grounding capacity), which is formed with the phase line and the neutral line busbar to form the TN-S grounding system.
ING grounding system is a traditional method, which is well known, but there are problems such as high cost and poor effect. The IGB grounding system technology represented by Schneider Electric's Merck busbar trunking is an improvement and technical renewal on the basis of traditional methods. It not only overcomes the disadvantages of traditional ING systems, but also has many advantages that traditional ING can not compare with, so that the entire grounding system is safer and more reliable. Busbar trunking manufacturers that usually use IGB practices meet the requirements of UL857, IEC439 and GB7251, and use aluminum plates of electrical grade as IGB (the shell of the busbar trunking system), and choose the appropriate section to make the capacity of the IGB grounding current circuit more than 50%.
IGB advantages over ING
1) The protection is comprehensive, the grounding path is direct, and the grounding path is short. The ING grounding busbar (PE) is located on one side of the busbar slot in Figure 1, which means that only a small part of the live parts are separated from the human body by the grounding system, and the grounding system only protects one side of the busbar slot, and there is no protection for the other three sides. That is, only the leakage current of phase A can directly flow into the ING and introduce it into the ground, while the leakage current of other phase lines must flow through the shell to the ING, and then introduce it into the ground. Therefore, the ING grounding protection is not comprehensive, the grounding path is not direct and long. All phase lines and neutral lines of IGB are included in the IGB grounding busbar (see Figure 2), which completely separates the live parts from the human body, and all four sides of the busbar slot are protected. Therefore, all live parts leakage current can directly flow through the IGB into the ground, and the grounding protection is very comprehensive, the grounding path is very direct, and the path is very short.
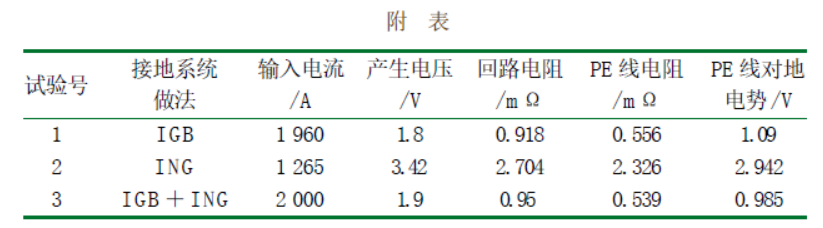
2) The grounding resistance is small and the potential to ground is small. In 1993, the relevant departments in Singapore conducted a test, selecting 20 in (about 6 m, 2 segments, 3 joints), 1 600 A busbar (the grounding system is IGB), and using a special current source to input simulated fault current into the busbar system. The grounding systems (PE) of ING, IGB, and ING + IGB were tested to detect the grounding resistance and potential to ground when the fault current passed through these three grounding systems and compared them (the test results are shown in the appendix). The above test results show that the grounding system circuit resistance formed by the IGB is very small, the potential to ground is very low, and the safety is good. However, the grounding system circuit resistance formed by the traditional ING is large, the potential to ground is high, and the safety is poor. If IGB and ING are used together, more than 80% of the current flows through IGB, and only 20% of the current flows through ING, indicating that IGB has a better fault current carrying capacity than ING.
3)The grounding path resistance is small and the potential of the shell to the ground is small. When a leakage fault occurs in the phase line, the leakage current of the ING grounding system flows from the phase line → shell → ING → ground, making the grounding path resistance large (the ordinary metal shell and ING resistance are both large), and at the same time, it makes the potential of the shell to the ground rise, greatly increasing the harm to the human body. However, the IGB grounding system, the leakage current flows from the phase line → IGB → ground, making the grounding path resistance very small (the IGB resistance is small), and at the same time, it makes the potential of the shell (i.e. IGB) to the ground very low, greatly reducing the harm to the human body.
4) IGB can greatly save the cost of busbar manufacturing (no dedicated grounding busbar is required in the busbar slot), thereby reducing the cost of busbar slots and making the product more competitive in the market. In summary, compared to ING, IGB provides a more effective and safe grounding path, providing a more reliable guarantee for the safe use of busbar trunking systems. Now IGB has become the grounding system solution for busbar trunking, and has been adopted by foreign brand busbar trunking factories such as Schneider Electric and Merlin Gerin.